Distributed ledgers have revolutionized the way we conduct transactions and share information. With the advent of blockchain technology, we have witnessed a significant shift in the financial industry, where decentralized digital currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum have gained mainstream acceptance. However, as the demand for faster, more secure, and more efficient systems increases, alternative solutions to blockchain technology have emerged, one of which is hashgraph technology.
In this article, we will compare hashgraph vs blockchain technology in detail, pointing out the main differences between the two and the ways they could be used.
Introduction
Distributed ledgers are computerized databases that store and share information across a network of computers. Distributed ledgers are different from traditional centralized systems in that they allow multiple parties to access and update the same information in a safe and open way. This makes distributed ledgers ideal for various applications, including financial transactions, supply chain management, and identity verification.
Blockchain technology is one of the most well-known types of distributed ledgers. It was first used in 2008 as a safe and clear way to send and receive digital currency. Since then, blockchain technology has evolved, and its potential applications have expanded beyond digital currencies to include smart contracts, decentralized applications, and more.
However, blockchain technology has its limitations. One of the main drawbacks is its scalability, as the system becomes slower as more nodes are added to the network. Hashgraph technology is one of the substitutes for blockchain technology that has emerged as a result of this.
Hashgraph Technology
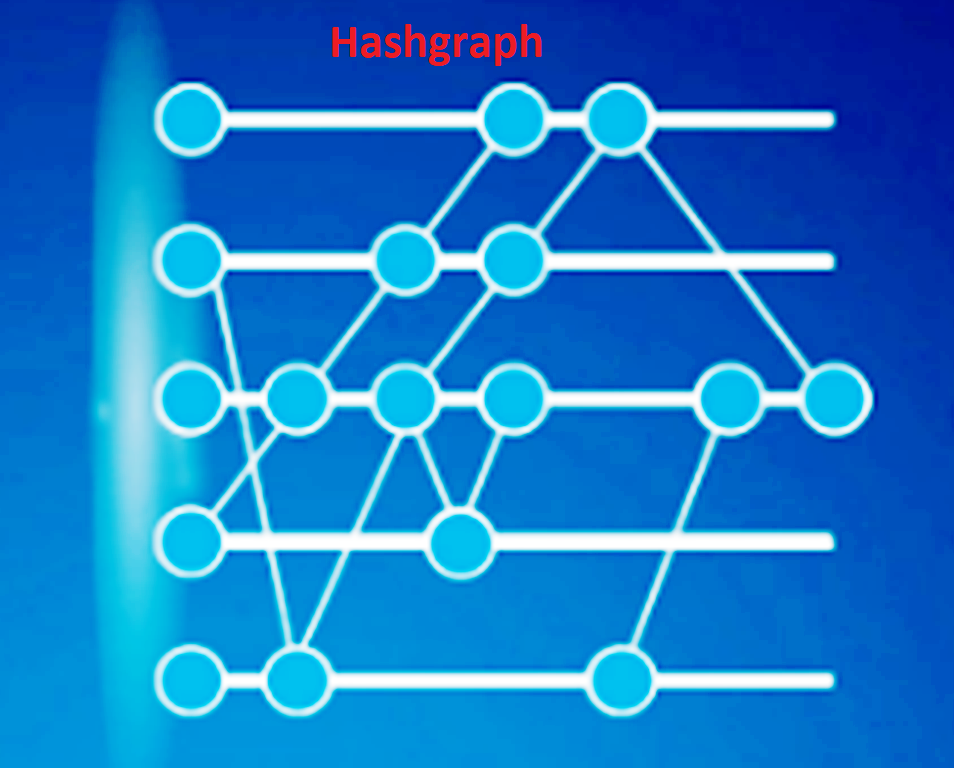
Hashgraph technology is a distributed ledger that was first introduced in 2015. It is a consensus mechanism that uses a directed acyclic graph (DAG) to enable faster transactions and more efficient consensus. Hashgraph technology uses a gossip protocol to spread information throughout the network, ensuring that all nodes have the same information and that consensus is reached in a timely manner.
How Hashgraph Technology Works
Hashgraph technology works by using a gossip protocol to spread information throughout the network. When a user creates a transaction, the transaction is broadcast to a random node in the network. The receiving node then gossips the transaction to other nodes in the network, and so on, until all nodes have received the transaction.
Once all nodes have received the transaction, they use a virtual voting algorithm to reach consensus on the order of the transactions. This consensus mechanism is more efficient than the proof-of-work (PoW) algorithm used by blockchain technology, as it does not require extensive computational power or energy consumption.
Advantages of Hashgraph Technology
- Speed: Hashgraph technology is faster than blockchain technology, as it can process up to hundreds of thousands of transactions per second.
- Efficiency: Hashgraph technology is more energy-efficient than blockchain technology, as it does not require extensive computational power to reach consensus.
- Fairness: Hashgraph technology is more fair than blockchain technology, as all nodes have equal influence over the consensus process, eliminating the possibility of mining cartels or centralization.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is a distributed ledger that was first introduced in 2008. It is a consensus mechanism that uses a PoW algorithm to reach consensus on the order of transactions. Blockchain technology uses blocks to store transactions, and each block is linked to the previous block, forming a chain of blocks (hence the name blockchain).
How Blockchain Technology Works
A consensus is reached on the sequence of transactions using a PoW algorithm, which is how blockchain technology operates. When a user creates a transaction, the transaction is broadcast to the network. Miners then compete to validate the transaction by solving complex mathematical puzzles. Once a miner solves the puzzle, the transaction is added to a block, which is then added to the blockchain.
The PoW algorithm is resource-intensive, as it requires miners to use significant computational power to solve mathematical puzzles. This has led to concerns about the energy consumption of blockchain technology, as the mining process requires significant amounts of electricity.
Advantages of Blockchain Technology
- Security: Blockchain technology is highly secure, as all transactions are verified and recorded in a tamper-proof manner. A transaction can neither be changed nor erased once it has been added to the database.
- Decentralization: Blockchain technology is decentralized, as no single entity controls the data. This lowers the possibility of fraud or corruption and eliminates the need for middlemen.
- Transparency: Blockchain technology is transparent, as all transactions are publicly visible on the blockchain. This minimizes the possibility of confusion or disagreements by ensuring that all parties have access to the same information.
Comparison between Hashgraph and Blockchain
Scalability
One of the main differences between hashgraph and blockchain technology is their scalability. Hashgraph technology is more scalable than blockchain technology, as it can process up to hundreds of thousands of transactions per second, whereas blockchain technology can process only a few transactions per second. This is because hashgraph technology does not require the extensive computational power and time-consuming mining process required by blockchain technology.
Speed
Hashgraph technology is also faster than blockchain technology, as transactions can be processed in a matter of seconds. This is because hashgraph technology uses a gossip protocol to spread information throughout the network, allowing for faster consensus. Blockchain technology, on the other hand, can take several minutes or even hours to process a transaction, as the mining process can be time-consuming.
Consensus Mechanisms
Hashgraph technology uses a virtual voting algorithm to reach consensus, whereas blockchain technology uses a PoW algorithm. While both algorithms are designed to ensure that all nodes in the network agree on the order of transactions, the virtual voting algorithm used by hashgraph technology is more efficient and energy-efficient than the PoW algorithm used by blockchain technology.
Security
Both hashgraph and blockchain technology are secure, as all transactions are verified and recorded in a tamper-proof manner. However, blockchain technology is more secure in terms of immutability, as once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. In contrast, hashgraph technology allows for some degree of flexibility in terms of transaction ordering, which could potentially make it more vulnerable to attacks.
Energy Efficiency
Hashgraph technology is more energy-efficient than blockchain technology, as it does not require extensive computational power to reach consensus. This is because hashgraph technology uses a virtual voting algorithm, which is more efficient than the PoW algorithm used by blockchain technology. As a result, hashgraph technology has a lower carbon footprint than blockchain technology.
Potential Applications for Hashgraph and Blockchain
Both hashgraph and blockchain technology have the potential to transform various industries, including finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and more. Hashgraph technology’s high scalability and speed make it ideal for applications that require fast and efficient transactions, such as micropayments, gaming, and social media. On the other hand, blockchain technology’s high security and immutability make it ideal for applications that require a high degree of trust, such as identity verification, land registry, and voting systems.
Video: Blockchain vs Hashgraph, what is the difference?
Conclusion
Hashgraph technology and blockchain technology are both distributed ledgers that have the potential to transform various industries. While both technologies have their advantages and drawbacks, it is clear that hashgraph technology is more scalable, faster, and energy-efficient than blockchain technology. But blockchain technology is more secure and can’t be changed. This makes it perfect for applications that need a lot of trust. As the demand for faster, more secure, and more efficient systems increases, we may see the emergence of hybrid solutions that combine the best of both technologies to create distributed ledgers that are scalable, fast, secure, and energy-efficient.